Fundamental Insights
#1 Technique design of bridges
There are three kinds of bridges:
- Local Verification
- External Verification
- Native Verification
Local Verification
Hash Time Lock Contract (HTCL) is the most common method in local verification. The is one of the oldest solutions and the easiest one to implement.
HTCL is easy to implement, supports the atomic transaction, and, most important, it is trustless. It does have a few limitations. HTCL faces scalability issues because it is P2P. In real-life, users will be hard to transfer a large number of tokens to another chain, because the user cannot find his/her counterparty. Another problem is that it cannot support complex use cases like cross-chain messages.
External Verification
The cross-chain protocol relies on external relayers to pass messages from the source chain to the destination chain. To increase the decentralization, robustness, and safety, there is a relayer network to deliver the transactions. After reaching the consensus in the relayer network, the message will be passed to the destination chain. The whole relayer network performs like a multi-sig wallet.
The problem with this approach is decentralization and safety. The users need to trust the relayer network. The nodes in the relayer network are often bonded. However, the slashing condition is hard to calculate. Thus safety is not guaranteed.
Native Verification
In this model, there is a light client running on the destination chain which can validate and read events or states on the source chain. After the blocker headers and transactions relaying to the destination chain, the light client can verify the validity natively on the destination chain.
This approach is relatively safe and trustless. Users don’t need to trust the intermediary entities, because the light client can verify the validity. However, this approach costs a lot, especially running a light client on Ethereum. Also, it is development intensive. The cross-chain protocols need to build light clients for every supported chain.
Native verification is the most promising one and the ZK bridge belongs to this category.

(1) =nil; Foundation (@nil_foundation) / Twitter
Nil Foundation is working on the frontier of ZK bridges. It recently published the cross-chain infra from Mina to Ethereum and Mina to Polygon.
In one word, this infra allows smart contracts on Polygon or Ethereum to verify the validity of Mina state. With this infra, smart contracts have the ability to recognize invalid cross-chain tx.
This infra can generate Mina state proof and smart contracts on Polygon and Ethereum can verify the proof onchain. In the future, cross-chain apps can directly verify the cross-chain tx validity with this infra. For example, apps can use this infra to verify the tx validity passing from the relayers. We are moving from using game theory to math to ensure the validity of cross-chain tx.
In the demo, it takes around 1 min to generate the proof and costs 2.5m gas to verify it. If the gas price is 80, this costs 0.5 ETH for verification on Ethereum.
In the future, more EVM chains will be able to verify the Mina state proofs onchain. However, it is not feasible to generate Ethereum state proofs and verify on the Mina onchain.
#2 Ape into the journey of BAYC
The beginning of this magic trip
Yuga Labs is a Web3 company and BAYC consists of 10,000 programmatically generated, exclusive NFT collectibles consisting of 170 different combinations of features. The "BAYC" went on sale on April 23, 2021, at a price of 0.08 E. At first, BAYC did not receive much attention. On May 1, when Pranksy, a well-known collector, took notice of the project and announced that he had purchased more than 250 apes. From the moment he posted his twitter, the number of sales and users of BAYC skyrocketed. After only 117 minutes, BAYC sold out.

ApeCoin is an ERC-20 Token used for governance and buying and selling within the Ape ecosystem. Holders can participate in the ApeCoin DAO, buy and sell with other participants, and gain access to exclusive ecosystem services, game events and items. In the Ape Foundation, the foundation layer of the ApeCoin DAO is responsible for the usual governance and project management within the ecosystem. The fund pays the Ape Foundation's costs as directed by the DAO and serves as the infrastructure for ApeCoin holders to participate in the governance process. Yuga Labs has limited the availability of ApeCoin to 1 billion Token, which are gradually unlocked over a 48-month. 150 million Token are airdropped directly to BAYC and MAYC holders at launch, while a total of 470 million Token are airdropped to BAYC and MAYC holders at launch. A total of 470 million Tokens will serve as the DAO's vault and ecosystem resource. Initially, 117.5 million Tokens will be unlocked, and 730W Tokens will be unlocked each month for four years.
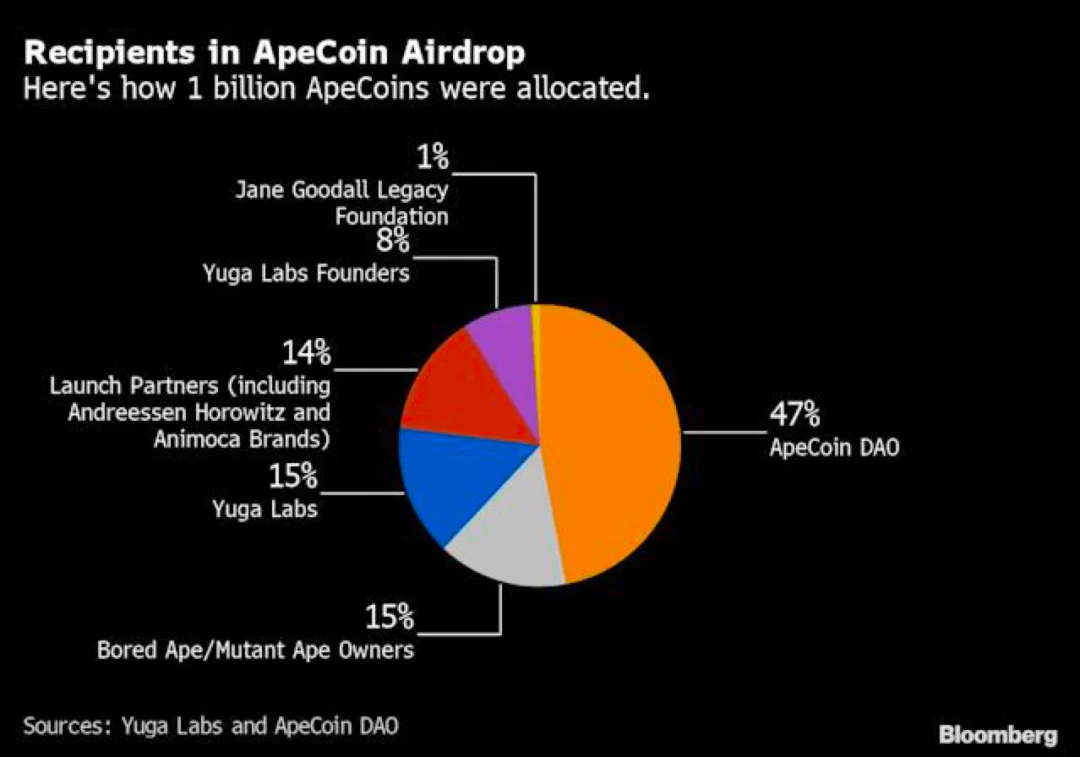
De-Collab Business Model
The team uses the De-Collab business model, with an ongoing commitment to bringing utility to community members. The decentralized collaborative model grants full business commonsense rights to individual BAYC holders. It allows holders to use, copy, display and produce derivative works of the NFTs they purchase. Thus, holders do not need to obtain any approval from the issuer and can fully commercialize their intellectual property rights. Through this approach, innovation is prioritized rather than horizontally controlled. This bottom-up approach has led to multiple spin-off projects that appear in a wide range of entertainment, music, fashion, games, and virtual worlds.
A sense of community belonging
BAYC's rapid progress cannot be separated from what uses the community has. Since its release in April, the BAYC project has grown into a large community in a short period of time by leaps and bounds. For the players who hold BAYC, it is more than a collector's item, it is a clubhouse. BYAC represents a network culture of crypto preferences who believe in the scope and see many applications of the technology in industries such as art, music, gaming and entertainment. This belief makes people want to join a community that shares the same values and beliefs. Belonging has always been a vital human need and BAYC members are currently the most dedicated and valuable NFT brand, at the forefront of innovation in the NFT range. In addition, it is a great feeling to share the same aesthetic and values with many celebrities.
#3 Talking about the DAO Valuation Framework: DAO as a form of state
What is a state - a group of people with a constitution and economic system? The same goes for DAOs or any Web3 community! Let's make an analogy to make it sound more convincing:
A country relies on its people to create "value" or "GDP" - DAOs rely on its community.
· States draft a constitution to make land laws. For DAOs, this charter is written into the rules of the smart contract.
· The state determines its political structure, and the associated governance and distribution of power, just as the Web3 community determines its governance and token distribution.

Now, let's try to demystify all these components and draw some analogies:
(C) Consumer Expenditure: In a country, every citizen spends money on their needs and luxuries. In the Web3 community, people usually spend their fiat/tokens to buy NFTs, transact on DeFi protocols, and these can essentially form the consumption part.
(I) Investing: Just as individuals and companies invest in a country, community members invest in community projects.
(G) Government spending: The government spends money for national welfare, just like DAOs can spend money to upgrade community functions, perform airdrops, etc. The DAO’s treasury balance can serve as another measure.
(XM) Exports minus Imports: Just like a country's exports or imports, Service DAOs may export their services, Investment DAOs may import services, etc. We can see a lot of transactions happening between DAOs in the near future.
Another way to measure a community’s GDP is to measure the “output” of the community:
- Distribution (how big is the DAO’s reach)
- Opportunities (how many DAO members have access to opportunities)
- Capital (how much capital is deployed)
Depending on the type of DAO, the output value will vary greatly, for example:
- Protocol DAO: The metrics here will be protocol specific, for example:
DeFi -> Total value locked
L1/L2 blockchain: unique wallets, transaction volumes
Consumer applications: revenue generated
- Service DAO: total revenue generated through services
- Social DAO: Collectibles Vault, Membership Income
- Investing in DAOs: Return on Investment (ROI), AUM (Assets Under Management)
- Media DAO: Channels that cover DAO, such as Podcast, Newsletter, etc.
Overall, the ratio between opportunity, distribution, and capital depends heavily on the type of DAO. For Media DAO, the distribution (influence) ratio is very high, while for Investment DAO, the capital ratio is very high.
Week's Recap
- Founders from a16z, Solana and more back new billion-dollar crypto fund
- Dragonfly Capital Raises $650M for Third Crypto Fund
- Decentralized exchange infrastructure provider 0x Labs raises $70 million
- Peter Thiel's Founders Fund co-leads $20 million Series A for Ondo Finance
- Gate Ventures on Track to Close $200M Crypto Fund by Q3
- Apeiron Secures 13.5M Seed Funding with Core Anchor Hashed
- Argent Raises $40M to Make Crypto Wallets Easier to Use
Indicator Tracking
Crypto Fear & Greed Index
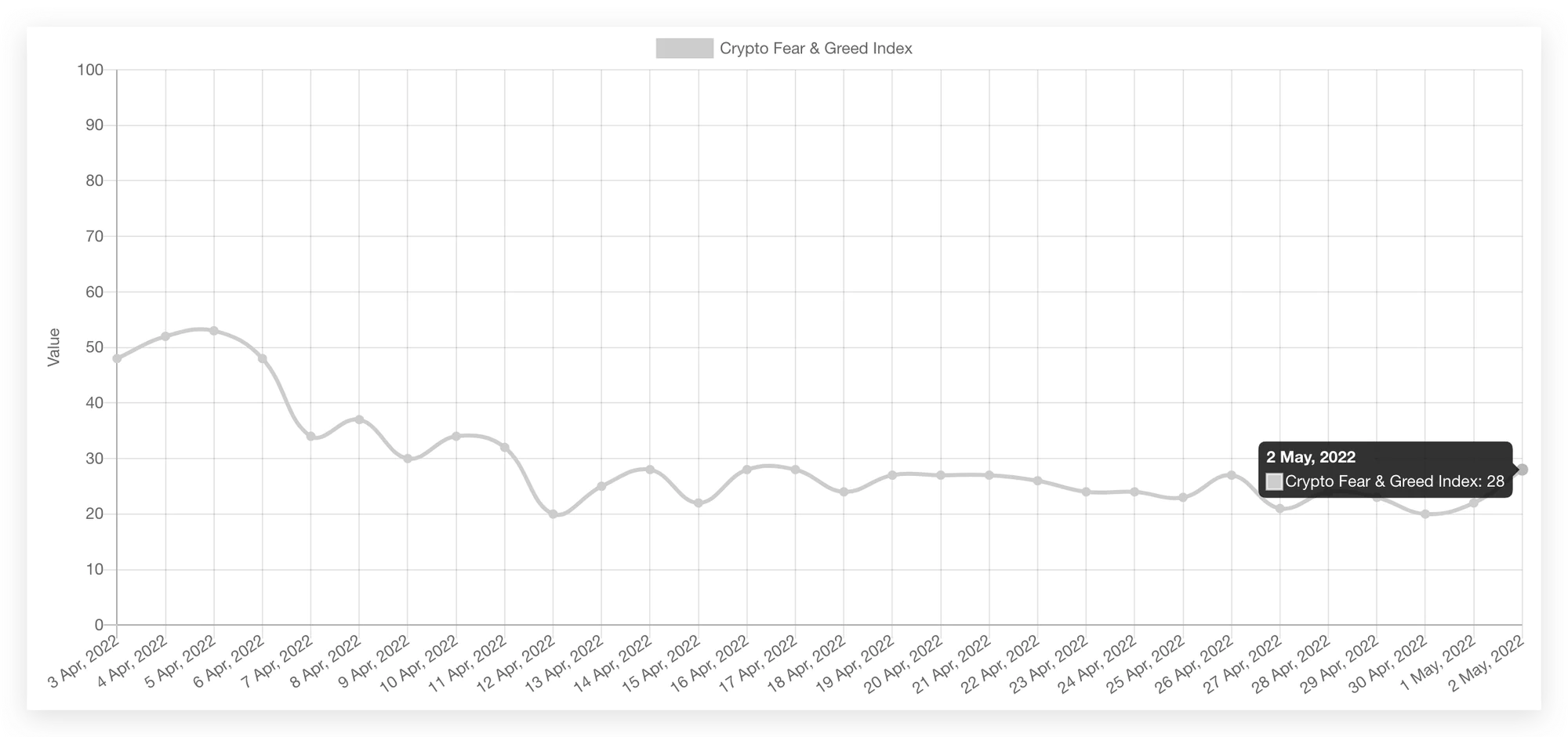
Source: Alternative
Data of NFT
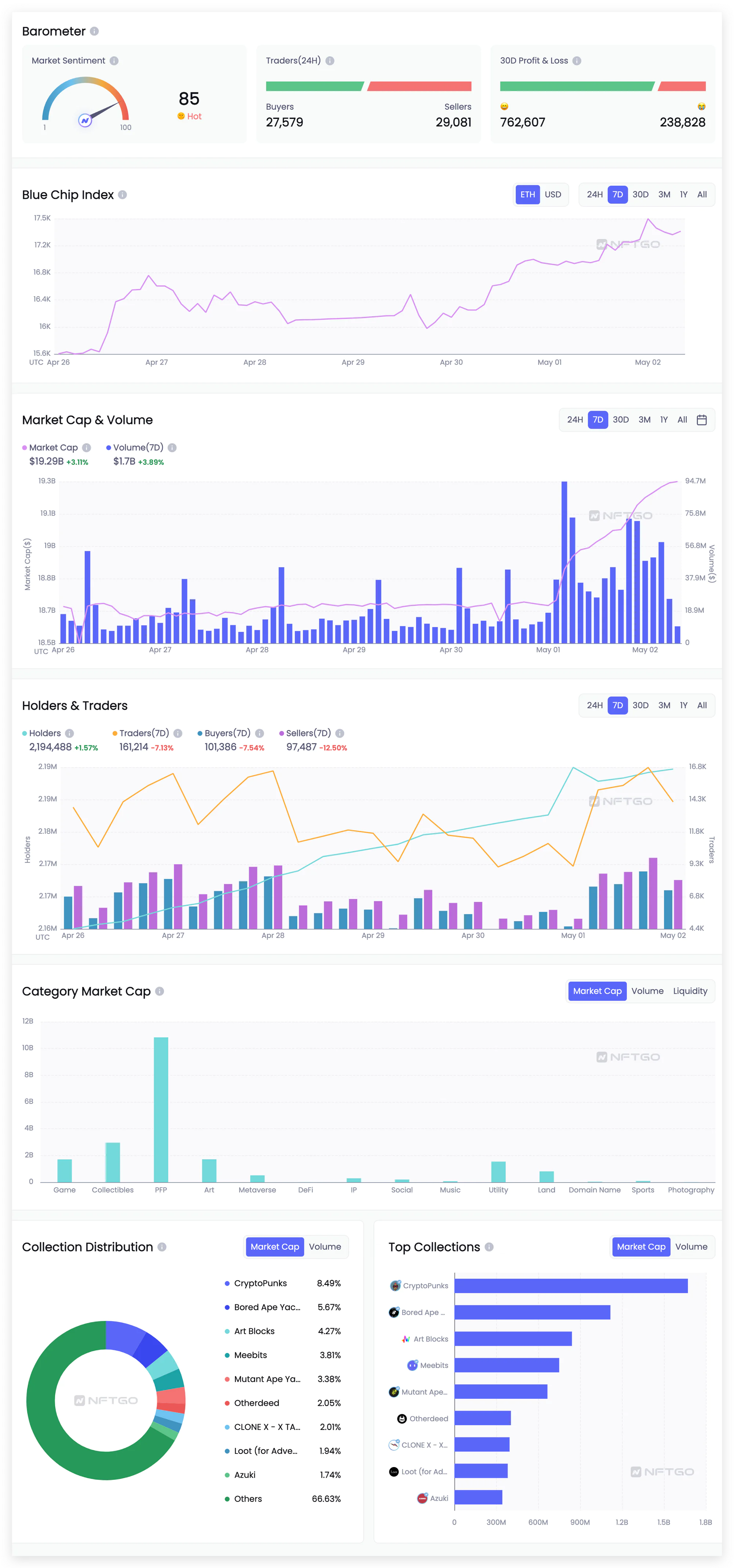
Source: NFTGo
Data of NFT Maketplaces
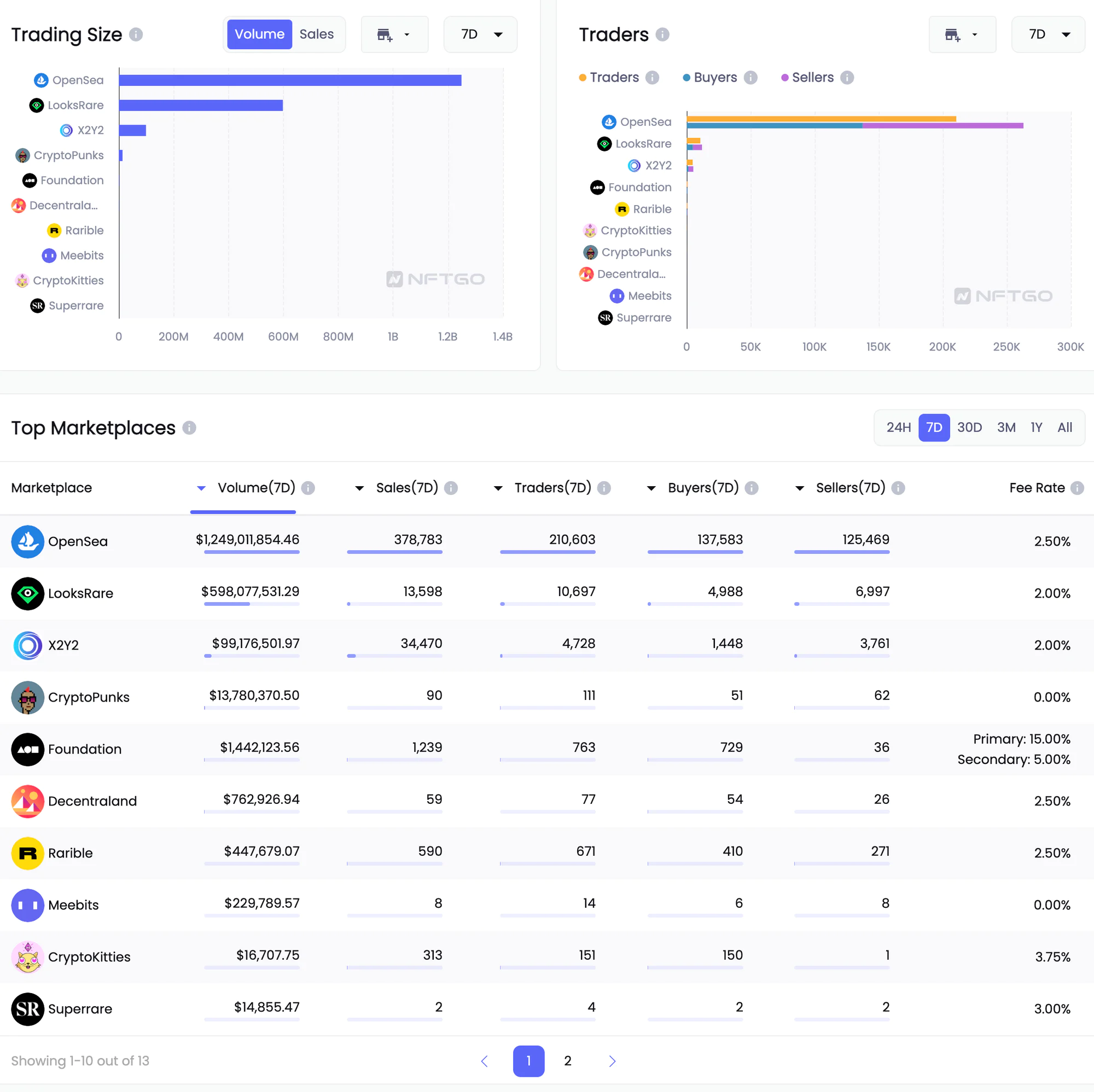
Source: NFTGo
Protocol Total Revenue
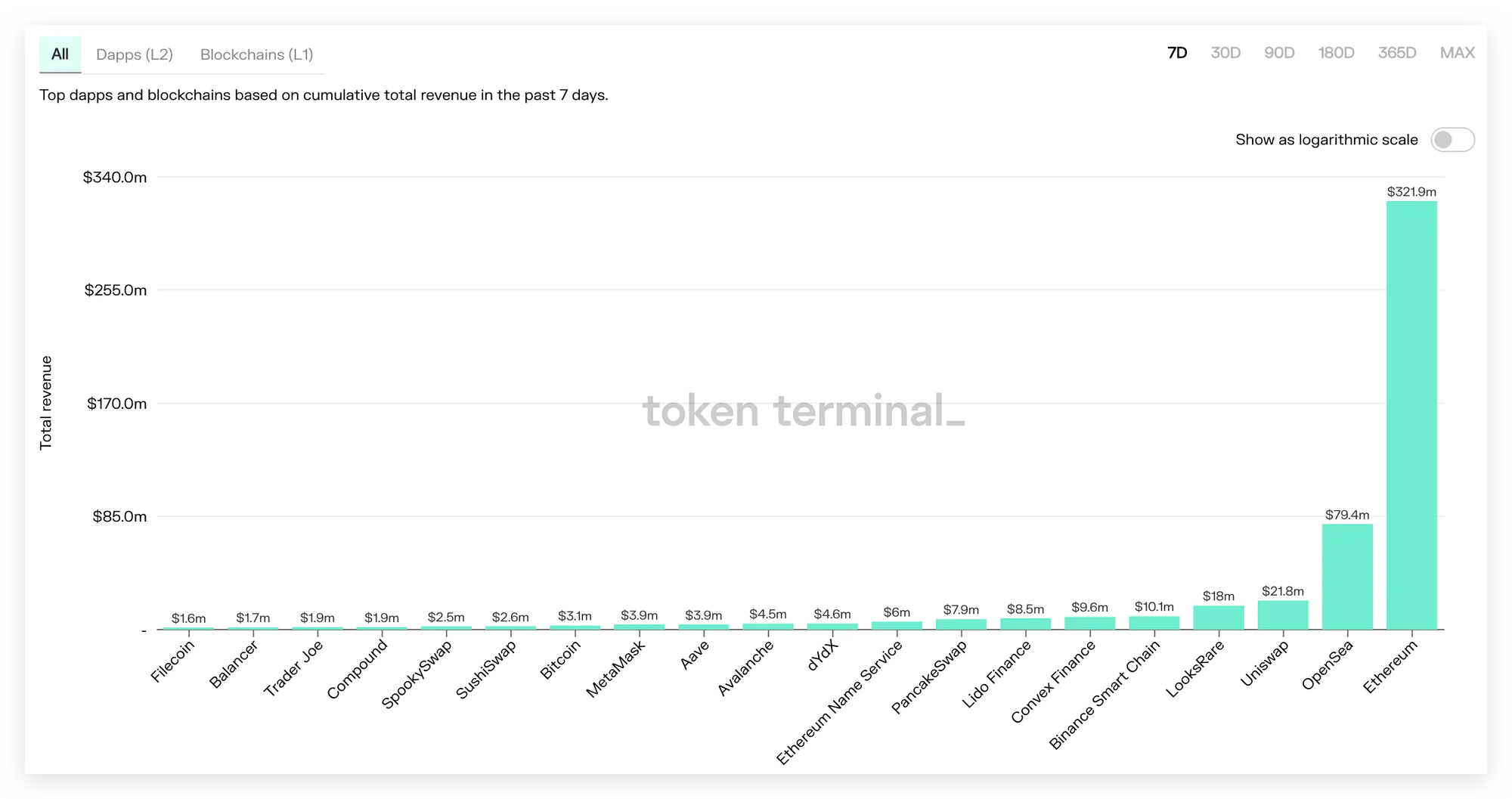
Source: Token Terminal